Have you ever felt lost trying to understand blockchain? You are not the only one. Most people hear “blockchain” and immediately think of confusing tech jargon. But at its core, a blockchain is just a shared digital ledger that keeps records safe.
I want to help you cut through the noise. We will look at exactly how this technology powers everything from Bitcoin to supply chains without the headache.
I’ll walk you through the key pieces like decentralized ledgers, nodes, and smart contracts. By the end, you will know exactly how it all fits together.
So, grab a coffee and let’s get started. I promise to keep it simple and practical.
Key Takeaways
Blockchain is a secure digital ledger distributed across many computers (nodes), a concept popularized by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009.
Data lives in blocks linked by cryptographic hashes (like SHA-256). If you change one character of data, the whole chain breaks, which makes tampering obvious.
Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum use consensus mechanisms to agree on truth. Proof of Work (PoW) uses massive energy, while Proof of Stake (PoS) reduces that consumption by over 99.95%.
Real-world wins are happening now. Walmart uses it to track food in 2.2 seconds (down from 7 days), and Propy has handled over $4 billion in real estate transactions.
Challenges remain. Bitcoin’s network processes only about 7-10 transactions per second compared to Visa’s 65,000. New rules like the GENIUS Act of 2025 are finally setting clear standards for stablecoins.
Table of Contents
What Is Blockchain Technology?
![How Does Blockchain Technology Work? [Ultimate Guide] Secure digital ledger.](https://www.geekextreme.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/infographic-How-Does-Blockchain-Technology-Work-Ultimate-Guide-413920-_0399.jpg)
Think of a blockchain as a Google Doc that is stuck in “View Only” mode for history but “Edit” mode for new lines. It is a digital ledger duplicated across a network of computers. No single person controls the file. Everyone gets a copy.
Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta first described this chain of cryptographically secured blocks in 1991. They wanted a way to timestamp documents so no one could backdate them.
In 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto applied this idea to money and created the Bitcoin protocol. This was the first time we solved the “double-spending” problem without a bank.
I like to visualize blocks as Lego bricks. Each brick (block) snaps onto the one before it. If you try to pull out a brick from the bottom, the whole tower (chain) collapses. Each block holds transaction details—like who sent money to whom—and a unique digital fingerprint.
This structure makes the ledger immutable. Once a block is added, you cannot change it. This stops fraud cold because everyone on the network would instantly reject a tampered block.
If you track new crypto listings, you are seeing this technology in action every day. Public blockchains show you exactly where digital assets move in real-time.
Key Components of Blockchain

Every engine has parts that make it run. Blockchain relies on three main components to keep the system honest: blocks, nodes, and miners (or validators).
What Are Blocks in a Blockchain?
A block is just a digital container. It holds a batch of valid transactions. In the Bitcoin network, a block has a weight limit of 4 million weight units (roughly 1-4 MB of data).
Every block contains three critical things:
- The Data: This includes the receiver, sender, and amount for standard transactions.
- The Hash: This is the block’s unique ID, generated by a cryptographic hash function.
- The Previous Hash: This points to the block before it. This link is what creates the “chain.”
When a block is filled, it gets sealed with a timestamp. The network locks it. Attempting to change a transaction inside a sealed block changes its hash. That breaks the link to the next block and alerts the entire network.
“Blocks are containers for truth—each chained by math and watched over by thousands.”
What Are Nodes and How Do They Work?
Nodes are the computers that run the blockchain software. They are the guardians of the ledger. You can even run one yourself using simple hardware like a Raspberry Pi 4 with a 1TB SSD.
I have set up nodes before using Bitcoin Core for bitcoin. It costs about $200 in hardware and connects you directly to the network.
Nodes have two main jobs:
- Storage: They keep a full copy of the entire blockchain history. As of late 2025, a full Bitcoin node stores over 650 GB of data.
- Validation: They check every new transaction against the rules. If someone tries to spend coins they don’t have, the nodes reject it.
In a peer-to-peer network, nodes talk to each other constantly. They spread new information across the globe in seconds. This decentralization means there is no central server for hackers to attack.
How Does Cryptographic Hashing Secure Data?
Hashing is the magic glue of blockchain. It takes any amount of data and turns it into a fixed-length string of characters. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm.
Here is why it works: The output is unique to the input. If you hash the text “Hello World”, you get a specific string. If you change it to “Hello World!” (adding just an exclamation mark), the hash changes completely. This is called the avalanche effect.
Because each block stores the hash of the previous block, a hacker cannot just change one record. They would have to re-calculate the hash for that block and every single block that came after it. Doing this on a large network like Bitcoin is mathematically impossible with current computers.
What Are Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain?
Since there is no boss, the nodes need a way to agree on the truth. This is called consensus. It prevents chaos and ensures everyone has the same ledger.
The two big players are: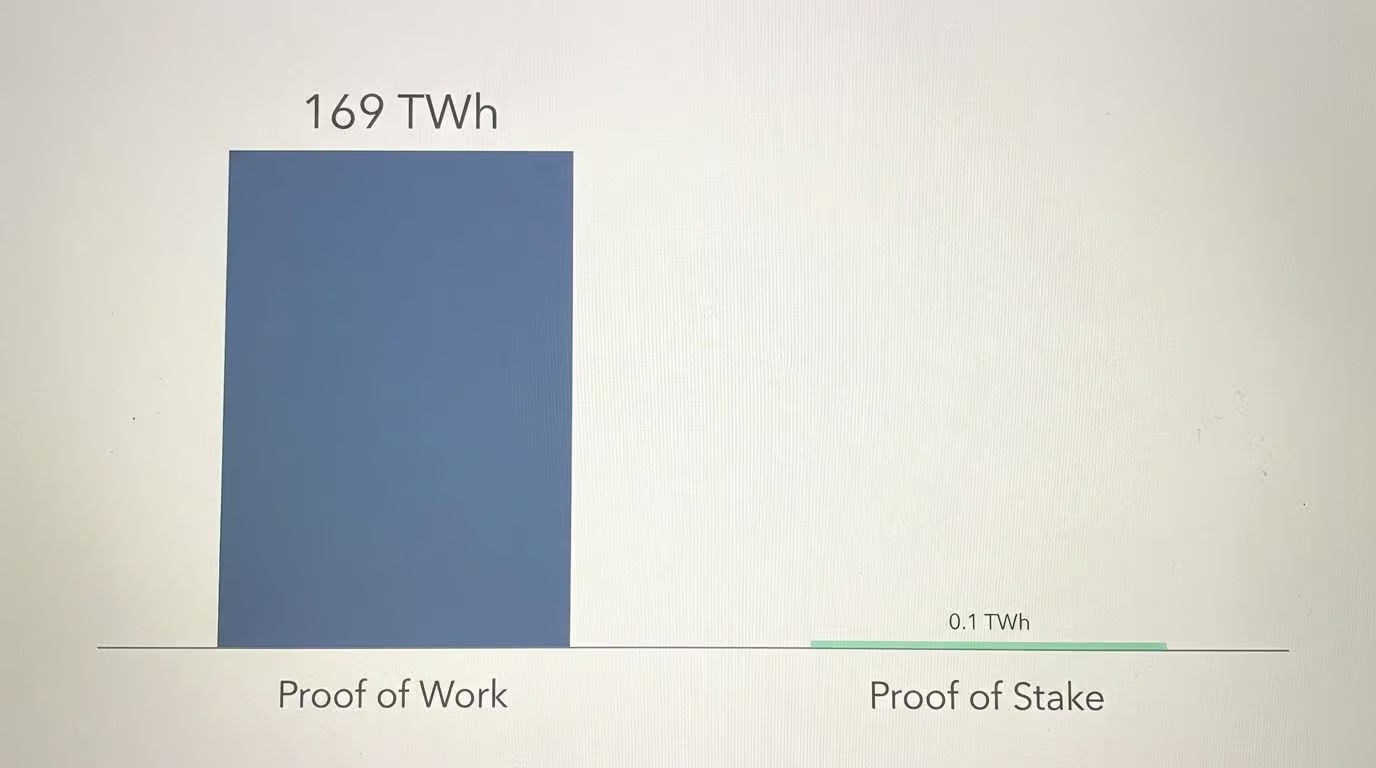
| Mechanism | How It Works | Energy Use |
|---|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Miners race to solve math puzzles. Used by Bitcoin. | High (Approx. 169 TWh/year) |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | Validators stake coins to secure the network. Used by Ethereum. | Low (99.95% less than PoW) |
I find it fascinating that PoS networks now have over 1.2 million validators securing Ethereum. It proves we can have security without burning the energy equivalent of a small country.
How Blockchain Technology Works
Let’s look at the actual journey of a transaction. It moves from your wallet to the permanent ledger in a few distinct steps.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D6j8RPvBccI
How Is a Transaction Recorded on the Blockchain?
When I send Bitcoin, I use a cryptocurrency wallet like Ledger or MetaMask to sign a message. This message broadcasts to the network.
It doesn’t go into a block immediately. It sits in a waiting room called the Mempool (memory pool). Miners pick transactions from this pool to build their next block. They prioritize transactions with higher fees, which in 2025 average around $0.82 but can spike during busy times.
How Are Transactions Verified on the Blockchain?
Once a miner selects my transaction, the race begins. In a Proof of Work system, the miner’s computer works furiously to solve a cryptographic puzzle.
They are looking for a specific number called a “nonce” that results in a valid hash. It is like trying to guess a combination lock by spinning the dials millions of times a second.
In Proof of Stake, the network randomly selects a validator to propose the block. Other validators then vote to attest that the block is valid. This process is much faster and requires standard computer hardware rather than specialized mining rigs.
How Is a New Block Created?
The miner who solves the puzzle first gets to create the block. They package the transactions, the previous block hash, and the nonce into a new bundle.
For their hard work, they receive a block reward. As of the 2024 halving, this reward is 3.125 BTC per block. This is the only way new Bitcoin enters the world.
Once created, the miner broadcasts the new block to all other nodes. The nodes check the work. If the math holds up, they add the block to their own copy of the ledger.
How Is a Block Added to the Blockchain?
This is the moment of truth. The new block snaps onto the end of the chain. It is now part of the permanent record.
Every node updates its distributed ledger to match. The transaction is now considered “confirmed.” For high-value transfers, I usually wait for six confirmations—meaning six more blocks have been added on top of mine. This makes the record mathematically irreversible.
How Is the Blockchain Secured?
Security comes from the cost of cheating. To rewrite history, an attacker would need to control 51% of the network’s computing power.
With Bitcoin’s hashrate hitting over 950 million terahashes per second in 2025, acquiring that much hardware is virtually impossible. It would cost billions of dollars and destroy the value of the currency the attacker is trying to steal.
I trust this system because it relies on greed and physics, not human honesty. The incentives are set up so that it is always more profitable to play by the rules than to break them.
Types of Blockchain
Not all blockchains are public. Companies and governments use different versions depending on their need for privacy versus transparency.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
Public blockchains are permissionless. This means anyone can join, read the ledger, and participate. Bitcoin and Ethereum are the prime examples.
I love these because they are truly censorship-resistant. No government or bank can shut down your account or freeze your funds. However, they can be slower because thousands of nodes have to agree on every single action.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
Private blockchains are permissioned. You need an invite to join. They are often used by businesses for internal record-keeping.
Hyperledger Fabric is a popular tool here. A company like Walmart uses this to track inventory. It is fast and private, but it is not decentralized. If the company decides to change a record, they technically can.

What Is a Hybrid Blockchain?
Hybrid blockchains try to offer the best of both worlds. They keep data private but use a public chain to verify integrity.
For example, a hospital might store patient records on a private server (for privacy) but anchor a hash of those records on a public blockchain. This proves the records haven’t been altered without revealing the sensitive data inside.
What Is a Consortium Blockchain?
A consortium blockchain is a group effort. Instead of one company running the show, a group of organizations shares control.
The Marco Polo Network for trade finance is a great example. Banks and corporations run the nodes together. This prevents any single bank from dominating the network while keeping the data secure from the general public.
Features of Blockchain Technology
Why do we use this tech? It boils down to four superpowers that traditional databases just don’t have.
What Does Decentralization Mean in Blockchain?
Decentralization removes the single point of failure. In a traditional system, if the bank’s server goes down, no one can transact. In blockchain, thousands of nodes hold the data.
We measure this using the Nakamoto Coefficient—the number of entities needed to compromise the system. A higher number means better decentralization. Bitcoin leads the pack here, making it incredibly resilient to shutdowns.
How Does Blockchain Ensure Transparency?
Transparency is absolute on public chains. I can go to a block explorer like Etherscan right now and see every transaction happening in real-time.
I can see the sender’s address, the receiver’s address, and the amount. I don’t see names, but I see the movement of value. This level of openness is unprecedented in the financial world.
Why Is Immutability Important in Blockchain?
Immutability creates trust. Once a record is six blocks deep, it is set in stone. This is critical for things like property deeds or supply chain records.
If I buy a house on the blockchain, I know the ownership record cannot be deleted by a corrupt official or a clerical error. The history is preserved forever.
How Does Blockchain Provide Security?
The security comes from cryptography. Your assets are protected by a private key—a complex password that only you know. Without that key, your funds are unmovable.
Even if a hacker breaches a crypto exchange, they cannot steal funds from your personal hardware wallet because they don’t have your physical device or your key. It puts the responsibility—and the safety—directly in your hands.
Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain
We touched on this earlier, but let’s look at the specific mechanisms that keep these networks running in 2025.
How Does Proof of Work (PoW) Function?
Proof of Work is the heavy lifter. It converts electricity into security. Miners spend energy to prove they have “skin in the game.”
While critics point to the 169 TWh of annual energy use (comparable to Poland), proponents argue this energy cost is what makes the network unhackable. It creates a physical barrier to entry for attackers.

What Is Proof of Stake (PoS) and How Does It Work?
Proof of Stake replaces miners with validators. You lock up (stake) your coins to vouch for the truth. If you try to cheat, the network burns your staked coins.
Ethereum’s switch to PoS reduced its carbon footprint by 99.95%. It is now green enough for corporate ESG standards, which has helped drive adoption by big institutional players.
How Does Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) Operate?
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is like a representative democracy. Token holders vote for a small group of “delegates” to validate transactions.
Networks like Tron and EOS use this. It allows for much faster transactions—often thousands per second—because fewer people need to agree. The trade-off is that it is more centralized than pure PoS or PoW.
What Is Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)?
PBFT is used in permissioned chains like Hyperledger Fabric. It relies on a pre-selected group of validators who know each other.
They vote in multiple rounds to agree on a block. It is incredibly fast and efficient but requires trust in the validators. It is perfect for corporate supply chains where all the participants are known business partners.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is not just for money anymore. I see it solving real problems in industries where trust and speed are missing.
How Are Cryptocurrencies Used?
People use crypto for everything from buying coffee to protecting their wealth against inflation. In 2025, Stablecoins like USDC have become massive for cross-border payments.
Instead of paying $30 for a wire transfer and waiting three days, I can send $10,000 in USDC for less than a dollar, and it arrives in seconds. This utility is driving real adoption in global trade.
How Is Blockchain Applied in Banking and Finance?
Banks are using blockchain to settle trades instantly. JPMorgan’s JPM Coin handles billions in daily transaction volume for wholesale clients.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) lets you lend, borrow, and trade without a bank. You can earn yield on your assets directly through smart contracts, cutting out the middleman who usually takes the profit.
What Role Does Blockchain Play in Supply Chain Management?
Walmart’s use of blockchain is the gold standard here. They reduced the time it takes to trace the origin of mangoes from 7 days to 2.2 seconds.
This speed saves lives during food safety recalls. If a batch of lettuce is contaminated, they can instantly identify exactly which farms it came from and which stores received it, without pulling safe product off the shelves.
How Is Blockchain Used in Healthcare?
In healthcare, patient data is often siloed. Blockchain puts the patient in control. Projects like MedRec are exploring ways to give patients a single, immutable record of their history.
This means you could visit a new specialist and grant them temporary access to your records instantly. No more faxing forms or carrying physical folders between offices.
How Does Blockchain Impact Real Estate?

Real estate is ripe for disruption. Platforms like Propy have facilitated over $4 billion in transaction volume by putting titles on-chain.
Their AI tool, “Agent Avery,” helps automate the closing process. By using smart contracts, we can automate escrow releases and title transfers, turning a 30-day closing nightmare into a smooth, transparent process.
How Does Blockchain Improve Voting Systems?
Voting needs to be secure and anonymous. Blockchain offers both. While full national elections are not there yet, West Virginia piloted blockchain voting for overseas military personnel back in 2018.
Today, DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) use tools like Snapshot to vote on protocol changes every day. The results are verifiable on-chain, proving that digital democracy is possible.
What Are Smart Contracts and How Do They Work?
A smart contract is “if this, then that” code. It executes automatically. Think of a vending machine: you put in money, you select a product, and the machine gives it to you. No clerk needed.
Ethereum popularized this. Developers write code in languages like Solidity. These contracts power everything from NFT marketplaces to complex lending protocols, automating agreements without the need for lawyers.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
The benefits go beyond just “it’s new tech.” It solves specific, expensive problems.
How Does Blockchain Enhance Security?
By removing the central point of failure, blockchain makes mass data breaches much harder. A hacker cannot just steal a database file because the “database” is split across thousands of computers.
The use of public/private key cryptography means that users are the only ones who can authorize actions on their accounts. It is a security model that puts the user first.
How Does Blockchain Improve Efficiency?
It removes the “middleman tax.” In traditional finance, clearing a stock trade takes two days (T+2) because intermediaries have to reconcile their ledgers. Blockchain does this instantly.
Settlement is immediate. When the transaction is confirmed, the asset has moved. This frees up capital that would otherwise be stuck in transit.
How Does Blockchain Help Reduce Costs?
Automating trust is cheaper than paying for it. Smart contracts replace administrative work. Supply chain tracking replaces manual audits.
For cross-border payments, blockchain cuts out the correspondent banking network. This can reduce fees by over 80% for international transfers, a huge win for businesses operating globally.
How Does Blockchain Increase Transparency?
It creates a shared source of truth. In supply chains, all partners see the same data. There is no “my spreadsheet vs. your spreadsheet.”
This shared visibility builds trust between partners who might not otherwise trust each other. They don’t have to trust the partner; they just have to trust the ledger.
Challenges of Blockchain Technology
Of course, it is not all sunshine and rainbows. We still have big hurdles to clear.
Why Does Blockchain Consume High Energy?
Bitcoin’s Proof of Work is energy-intensive by design. It uses about 169 TWh per year. While much of this comes from renewable sources (over 50% by some estimates), it is still a major point of criticism.
The industry is responding. Ethereum’s move to PoS and the rise of green mining initiatives are helping, but the energy narrative remains a barrier for some environmentalists.
What Are the Scalability Issues of Blockchain?
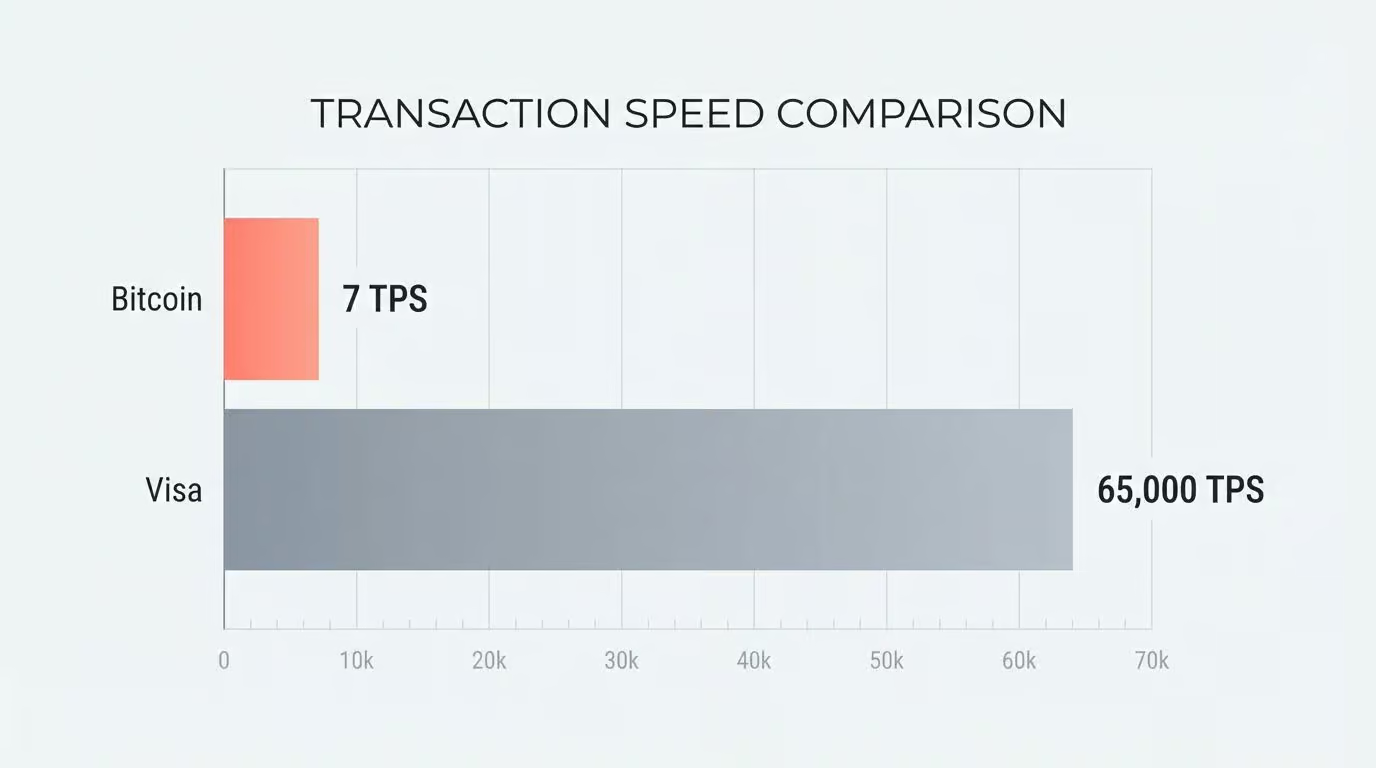
Blockchains are slow. Bitcoin handles ~7 transactions per second (TPS). Visa handles ~65,000. This is the “Scalability Trilemma”: you can have decentralization, security, and speed, but usually only two at a time.
Layer 2 solutions like Lightning Network and Arbitrum are fixing this. They process transactions off the main chain and bundle them up, allowing for thousands of TPS without sacrificing the main chain’s security.
What Are the Regulatory Concerns Around Blockchain?
Regulation is catching up. The GENIUS Act of 2025 recently established a framework for stablecoins in the US, requiring issuers to hold real cash reserves. This is good for safety but adds red tape.
We also saw the repeal of SAB 121, an accounting rule that made it hard for banks to hold crypto. The regulatory environment is shifting from “ban it” to “control it,” which creates uncertainty for builders.
How Does Blockchain Face Data Privacy Challenges?
Public blockchains are too transparent for some data. You don’t want your medical records on a public ledger. Privacy coins and Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK-Snarks) are the answer.
ZK-Snarks allow you to prove something is true (like “I am over 21”) without revealing the underlying data (your birthdate). This tech is crucial for bringing sensitive industries like healthcare on-chain.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Where do we go from here? The tech is maturing. It is becoming invisible infrastructure.
What Are the Latest Advances in Scalability Solutions?
Sharding is the next big upgrade for Ethereum. It splits the network into smaller pieces (shards) so nodes only have to verify a fraction of the data. This could push throughput to over 100,000 TPS.
Parallelized executions on chains like Solana and Monad are also pushing the boundaries, trying to make blockchain as fast as the traditional internet.
How Will Blockchain Integrate with Artificial Intelligence?
This is my favorite intersection. AI agents need a way to pay each other. They cannot open bank accounts. Blockchain provides the payment rails for AI.
Projects like Fetch.ai are building networks where AI agents can negotiate and trade data autonomously. If you are curious about the career side of this, check out this comparison of blockchain vs ai salary.
Which New Industries Will Blockchain Expand Into?
Gaming is huge. GameFi allows players to truly own their in-game items as NFTs. If you quit the game, you can sell your sword to another player for real money.
Carbon credits are another frontier. Putting carbon offsets on-chain ensures they are not double-counted, bringing integrity to the fight against climate change.
How Will Blockchain Technology Change in 2025?
By the end of 2025, I expect blockchain to fade into the background. You won’t know you are using it. You will just know your settlement happened instantly.
With Bitcoin’s hashrate at all-time highs and Ethereum’s validator count growing, the networks are more secure than ever. The focus now is on user experience—making wallets easier to use and transactions safer.
We are moving toward a world of self-sovereign identity and automated trust. It is a messy, exciting evolution, and we are just getting started.
People Also Ask
What is blockchain technology and how does it work?
I define it as a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) where a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes, validates every entry. Instead of a central database, the system groups data into blocks and seals them with a unique cryptographic hash like SHA-256 to create a permanent chain.
Why do people say blockchain is secure?
The security comes from its immutability and consensus mechanisms. Since every block contains the digital fingerprint of the previous one, altering a single record would require overpowering 51% of the entire network, which is mathematically nearly impossible.
Can you give an example of how blockchain works in real life?
If I send you Bitcoin, the network verifies the transfer purely through code, allowing the funds to settle in minutes without a bank like Chase holding it up for days.
Is blockchain only used for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin?
Definitely not; major companies like Walmart use the IBM Food Trust blockchain to track produce through the US supply chain in seconds. I also see it powering smart contracts on Ethereum, which are self-executing agreements that run without any need for lawyers or middlemen.
References
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772662223001844
https://www.theblock.co/learn/245697/what-are-blocks-in-a-blockchain (2023-08-28)
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp
https://hacken.io/discover/consensus-mechanisms/ (2025-06-30)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/blockchain
https://101blockchains.com/hybrid-blockchain/ (2021-01-28)
https://blog.cfte.education/consortium-blockchain-complete-guide/
https://www.starknet.io/glossary/what-is-decentralization-in-blockchain/ (2025-02-26)
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/proof-work.asp
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772427125002177
https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-proof-of-stake
http://pmg.csail.mit.edu/papers/osdi99.pdf
https://www.halborn.com/blog/post/what-is-practical-byzantine-fault-tolerance-in-blockchain (2023-06-10)
https://guides.loc.gov/fintech/21st-century/cryptocurrency-blockchain
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/23311975.2024.2407681
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772390923000227
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10701638/
https://trerc.tamu.edu/article/blockchain-and-real-estate/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319157822002221
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2667096824000934
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12599-020-00656-x (2020-06-19)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1084804521002307
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7390/12/23/3860
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s44227-025-00072-1
![How Does Blockchain Technology Work? [Ultimate Guide] 1 ALT text: Close-up of a laptop showing a digital ledger on the screen, placed on a wooden desk alongside a coffee cup, crumpled paper, notebooks, and pens in a cozy workspace.](https://www.geekextreme.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/digital-ledger-laptop-coffee-413920_0408.jpg)